When you have TMJ problems you may have difficulty doing things like eating and talking.
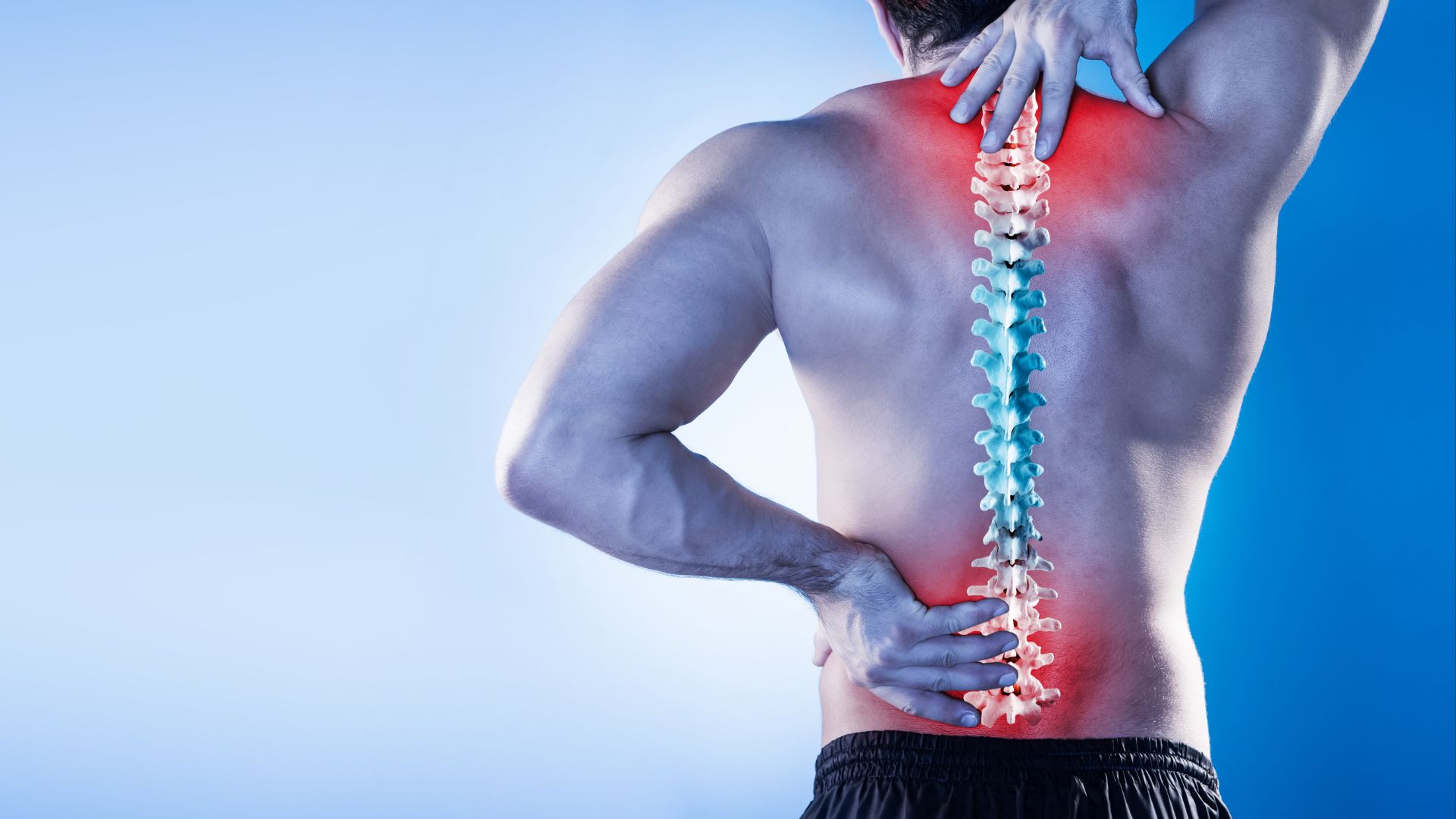
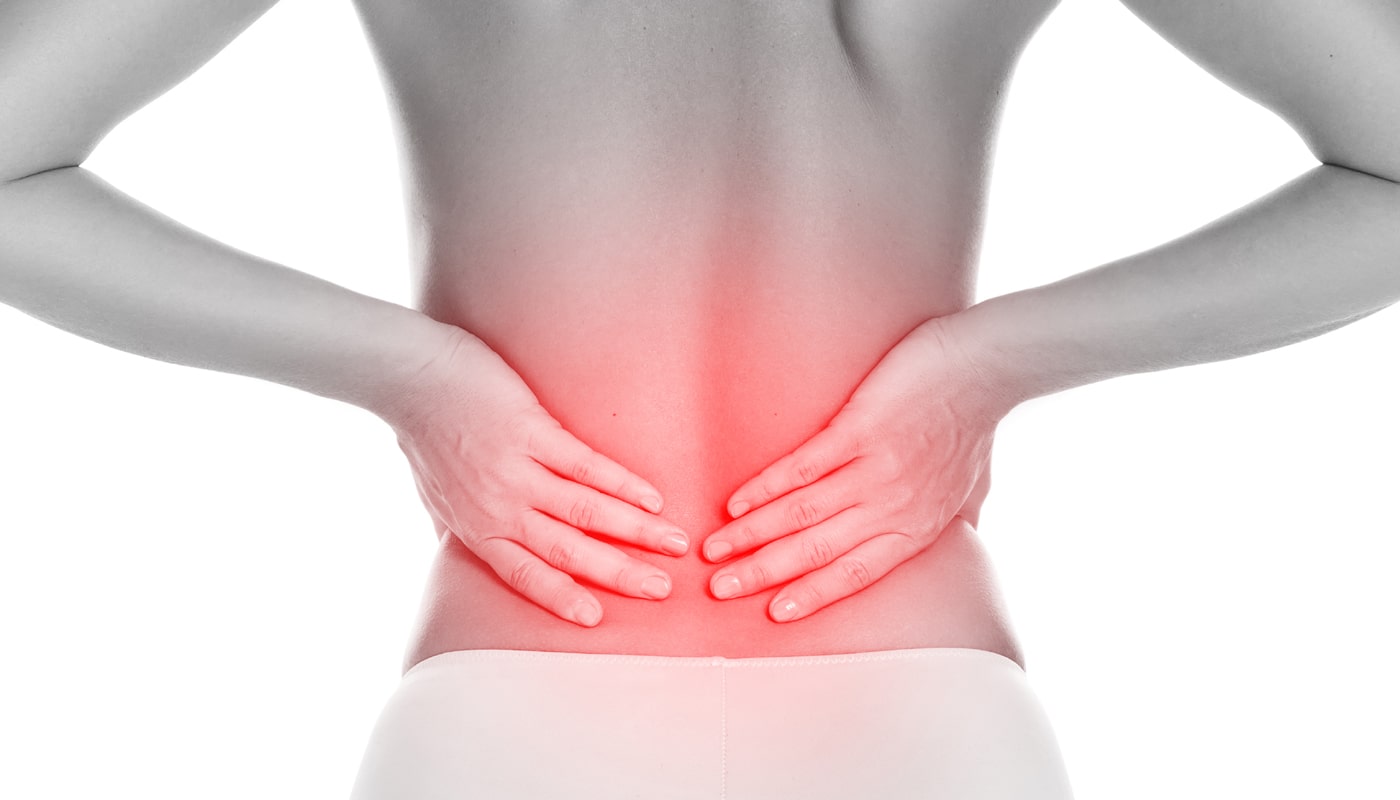
Low back pain is a common concern as almost everyone experiences back pain at least once in their lifetime.
Classification:
- By Duration: (acute, subacute, and chronic back pain)
- By Location: (upper, middle, or lower back)
- By Cause: (specific and non-specific back pain)
In non-specific back pain, no cause can be identified. On the other hand, specific back pain has a clear cause such as muscle tension, vertebral blockage, ISG syndrome, or a herniated disc.
Në çdo seancë fizioterapie, ne nuk trajtojmë vetëm simptomat, por punojmë për të gjetur shkakun e problemit, duke krijuar një plan të personalizuar që përshtatet me nevojat e çdo pacienti.
Studies
Classification of Back Pain Description
Low back pain, or lumbalgia, is a multidimensional pathology and can affect people of all ages. Back pain is classified according to several criteria:
Back pain is classified according to several criteria:
Localization
Duration
Depending on the duration of the complaints, it is determined whether the pain is acute, subacute, or chronic.
Information
Below we will list some of the main issues, pains, causes, categories, etc.
Acute back pain: Acute back pain occurs for the first time or after at least six months without pain and lasts a maximum of six weeks. The prognosis is generally good, and back pain improves within a few weeks for most people.
Subacute pain: If back pain lasts longer than six weeks up to three months, it is considered subacute.
Chronic back pain: Chronic back pain or recurrent chronic back pain lasts for more than three months. The severity of the pain can vary during this time – sometimes back pain is milder, sometimes it is more severe. Chronic back pain is more common with age.
Cause: Depending on whether or not there is a clear cause for the symptoms, a distinction is made between specific and nonspecific back pain.
Nonspecific back pain: In cases of nonspecific back pain, there is no clear cause for the symptoms. The overwhelming majority of all back pain cases have no specific cause.
In osteoporosis, the bones become increasingly brittle. They may fracture under minimal stress (such as falling or bumping into something). This often leads to vertebral body fractures, which are accompanied by back pain. The early stage of osteoporosis – osteopenia – can also be associated with back pain.
Many pregnant women experience back pain. There are several reasons for this. For example, hormonal changes in pregnant women cause tendons and ligaments in the pelvic floor area to loosen. This causes them to lose stability, which can lead to pain in the pelvis and lower back.
Specific back pain: Specific back pain has a clear identifiable cause. However, the cause does not necessarily come from the spine (as in the case of a herniated disc, for example). Instead, a wide range of diseases of other organs are often the reason for the discomfort in the back area. Below is a summary of important causes of specific back pain.
Muscle tension: Often, muscle tension is the cause of back pain. With poor posture, one-sided loading, and lack of movement, muscles become unevenly overloaded – some muscles are overburdened, others are tense. As a result, muscles shorten or stiffen, which can cause tension and pain.
Herniated disc: Intervertebral discs act as cushion-like shock absorbers between individual vertebral bodies. They consist of a soft, gel-like nucleus surrounded by a fibrocartilage ring. If there is narrowing of the intervertebral space, severe back pain may begin.
Spinal stenosis: The spinal canal runs through the vertebral column with the spinal cord located within it. This carries nerve signals from the brain to the body and back. In spinal stenosis, the spinal canal narrows in places, putting pressure on the spinal cord or developing nerve roots. The result is back pain, for example, in the sacral region.
Spondylitis (Ankylosing spondylitis): This is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease of the spine and the joint that connects the spine to the iliac bone (sacroiliac joint). The progressive disease causes deep back pain and can make the joints increasingly stiff over time. This is why ankylosing spondylitis is also called "ankylosing vertebral inflammation," which translates to “inflammation leading to vertebral stiffening.”
Vertebral slippage (spondylolisthesis): In this condition, the vertebrae are unstable, so they can easily shift. This mostly occurs in the lumbar region. Many affected people have no complaints or symptoms. However, back pain may occur, for example, during stress or certain movements. If a displaced vertebra presses on a nerve root, neurological deficits such as sensory disturbances or paralysis may also occur.